建立灵活动态的UI
编写:fastcome1985 - 原文:http://developer.android.com/training/basics/fragments/fragment-ui.html
如果我们的APP设计成要支持范围广泛的屏幕尺寸时,在可利用的屏幕空间内,我们可以通过在不同的布局配置中重用fragment来优化用户体验。
比如,一个手持设备可能适合一次只有一个fragment的单面板用户交互。而在更大屏幕尺寸的平板电脑上,我们可能更想要两个fragment并排在一起,用来向用户展示更多信息。
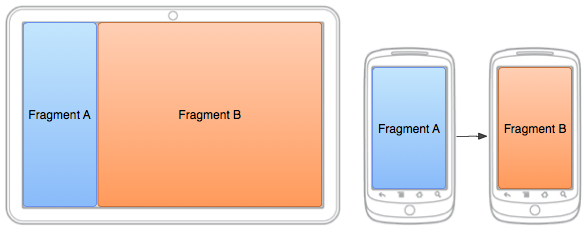
图1:两个fragments,在同一个activity不同屏幕尺寸中用不同的配置来展示。在大屏幕上,两个fragment被并排放置,在手持设备上,一次只放置一个fragment,所以在用户导航中,两个fragment必须进行替换。
- FragmentManager类为在activity运行时对fragment进行添加,移除,替换等操作提供了方法,来实现动态的用户体验。
在activity运行时添加fragment
比起用
<fragment>标签在activity的布局文件中定义fragment,就像上节课说的,我们还可以在activity运行时动态添加fragment,如果打算在activity的生命周期内替换fragment,这是必须的。为了执行fragment的增加或者移除操作,必须通过 FragmentManager 创建一个FragmentTransaction对象, FragmentTransaction提供了用来增加、移除、替换以及其它一些操作的APIs。
如果我们的activity允许fragment移除或者替换,我们应该在activity的onCreate()方法中添加初始化fragment(s).
运用fragment(尤其是那些在运行时添加的)的一个很重要的规则就是在布局中必须有一个容器View,fragment的layout将会放在这个view里面。
下面的这个布局是上节课的一次只显示一个fragment的布局的替代布局。为了替换fragment,这个Activity的布局包含了一个空的 FrameLayout作为fragment的容器。
注意文件名与上节课的布局一样,但是文件目录没有
large标识, 所以这一布局将会在比large小的屏幕上被使用,因为该屏幕无法满足同时放置两个fragments
res/layout/news_articles.xml:
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/fragment_container"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
- 在activity中,用Support Library APIs调用 getSupportFragmentManager()方法获取FragmentManager 对象,然后调用 beginTransaction()</a> 方法创建一个FragmentTransaction对象,然后调用add()方法添加一个fragment.
- 可以使用同一个 FragmentTransaction进行多次fragment事务。完成这些变化操作,准备开始执行改变时,必须调用commit()方法。
下例显示了如何添加一个fragment到之前的layout中
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity;
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.news_articles);
// Check that the activity is using the layout version with
// the fragment_container FrameLayout
if (findViewById(R.id.fragment_container) != null) {
// However, if we're being restored from a previous state,
// then we don't need to do anything and should return or else
// we could end up with overlapping fragments.
if (savedInstanceState != null) {
return;
}
// Create a new Fragment to be placed in the activity layout
HeadlinesFragment firstFragment = new HeadlinesFragment();
// In case this activity was started with special instructions from an
// Intent, pass the Intent's extras to the fragment as arguments
firstFragment.setArguments(getIntent().getExtras());
// Add the fragment to the 'fragment_container' FrameLayout
getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction()
.add(R.id.fragment_container, firstFragment).commit();
}
}
}
- 因为fragment是在activity运行时被添加进来时(不是在XML布局中用
<fragment>定义的),activity 可以移除这个fragment或者用另外一个来替换它。
替换Fragment
- 替换fragment的过程类似于添加过程,只需要将add()</a>方法替换为 replace()方法。
- 记住在执行fragment事务时,如移除或者替换,我们经常要适当地让用户可以向后导航与"撤销"这次改变。为了让用户向后导航fragment事务,我们必须在FragmentTransaction提交前调用addToBackStack()方法。
Note:当移除或者替换一个fragment并把它放入返回栈中时,被移除的fragment的生命周期是stopped(不是destoryed).当用户返回重新恢复这个fragment,它的生命周期是restarts。如果没有把fragment放入返回栈中,那么当它被移除或者替换时,其生命周期是destoryed。
- 下面是一个fragment替换的例子
// Create fragment and give it an argument specifying the article it should show
ArticleFragment newFragment = new ArticleFragment();
Bundle args = new Bundle();
args.putInt(ArticleFragment.ARG_POSITION, position);
newFragment.setArguments(args);
FragmentTransaction transaction = getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction();
// Replace whatever is in the fragment_container view with this fragment,
// and add the transaction to the back stack so the user can navigate back
transaction.replace(R.id.fragment_container, newFragment);
transaction.addToBackStack(null);
// Commit the transaction
transaction.commit();
- addToBackStack()方法提供了一个可选的String参数为事务指定了一个唯一的名字。除非打算用FragmentManager.BackStackEntry APIs来进行一些高级的fragments操作,这个名字不是必须的。